Getting a grip on stock market lingo can have a big impact on anyone who wants to invest in financial markets or trade stocks. We’ve put together a list of over 40 key stock market terms, starting with the most important and moving to the less critical ones. This guide aims to help you find your way through the tricky investing world with more confidence.
Short Summary
This article comprehensively lists 40+ essential stock market terms, ranging from fundamental concepts to advanced strategies. We explain each term in simple language, helping investors at all levels understand the stock market vocabulary. The list is organized from most important to least critical terms, making it easy for readers to prioritize their learning.
Stock Market Terms: Key Takeaways
- You need to grasp these terms to navigate the stock market well with guidance from
IFMC Institute - Begin with the basics and learn more complex ideas over time
- Using these terms often, as taught by IFMC, will boost your investing abilities
40+ Stock Market Terms: From Basics to Advanced Concepts
1. Stock

• A piece of a company you can own
• Shows you have a right to the company’s stuff and money it makes
2. Market Cap (Market Capitalization)
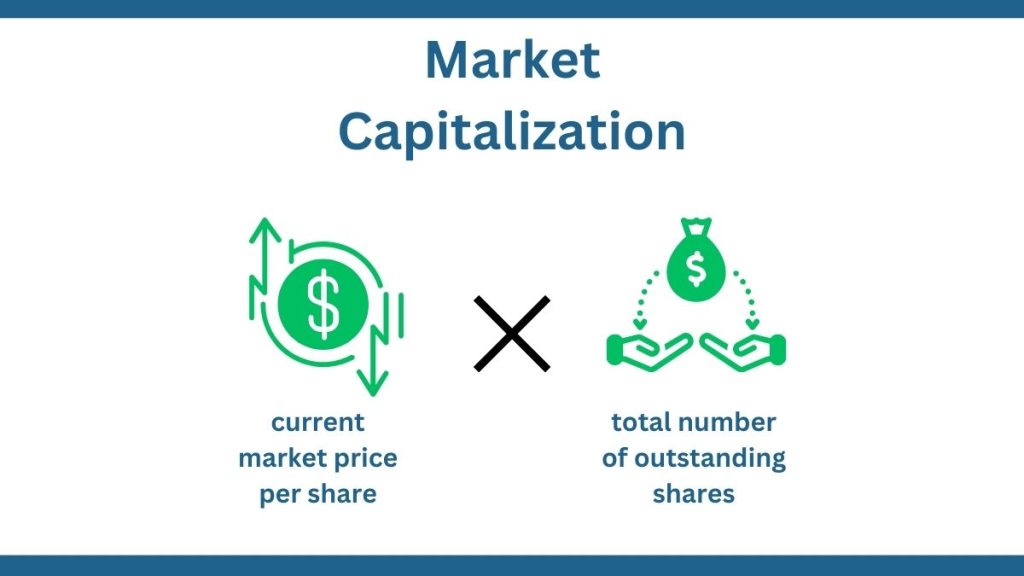
• How much all of a company’s shares are worth together
• You figure it out by multiplying all the shares by the price of one share now
3. Bull Market

• When stock prices go up and people feel good about buying
• People often say it’s happening when prices go up 20% from recent low points
4. Bear Market
• When stock prices drop and people don’t want to buy
• It’s usually called this when prices fall 20% from recent high points
5. Dividend
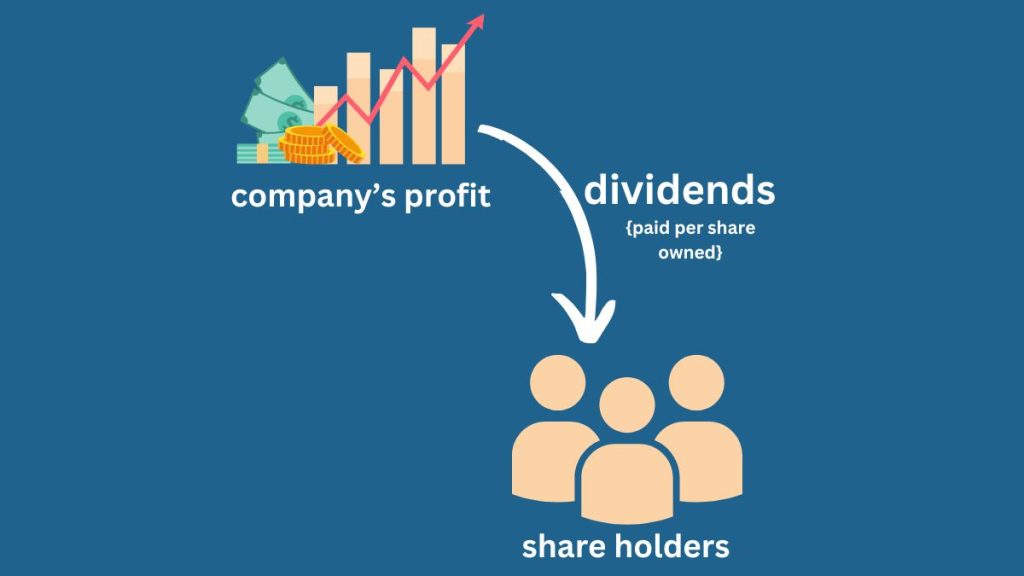
• What companies pay their shareholders from their profits
• Can be cash or more shares
6. P/E Ratio (Price-to-Earnings Ratio)

• Shows how a company’s stock price compares to its earnings per share
• Helps investors figure out if a stock costs too much or too little
7. Volume

• How many shares people buy and sell in a set time
• Shows how busy the market is and how easy it is to buy or sell
8. Volatility

• How much a stock’s price goes up and down
• When prices swing more, it means more risk but also a chance to make or lose more money
9. IPO (Initial Public Offering)

• A private company offers shares to the public for the first time
• This allows companies to get capital and gives investors new ways to invest
10. Broker

• A person or company that buys and sells for investors
• They might also do research and give money advice
11. Portfolio
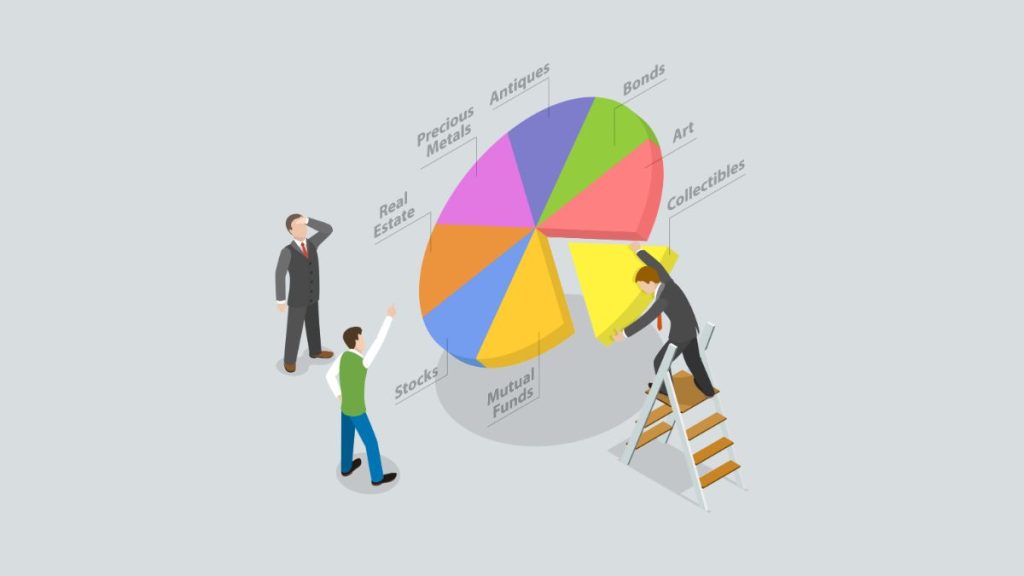
• A mix of investments that a person or group owns
• This can include stocks, bonds mutual funds, and other things you can invest in
12. Diversification

• Putting your money in different investments to lower risk
• This helps if one investment does, as others might still do well
13. Index

• Shows how a group of stocks performs
• The S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average are examples
14. ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund)

• An investment fund you can buy and sell on stock exchanges
• It often follows an index and helps spread out your investments
15. Mutual Fund
• A pro manages this investment pool, which combines money from many investors
• Mutual fund spreads out risk and gives you expert management
16. Blue Chip Stocks

• Shares from big well-known companies that have a track record of steady earnings
• People often think these are safer bets
17. Penny Stocks

• Cheap stocks that cost less than INR 50 per share
• They’re often linked to small companies and carry more risk
18. Margin

• Borrowing cash from a broker to buy stocks
• Can boost gains but also makes potential losses bigger
19. Short Selling

• Betting a stock will drop by borrowing shares and selling them hoping to grab them later at a cheaper price
• A way to make money when stock prices fall
20. Liquidity

• How easy it is to buy or sell something without changing its price
• More liquid assets come with less risk
21. Yield

• The money you get back from an investment shown as a percentage
• For stocks, this often means the dividends you receive
22. Market Order

• You tell your broker to buy or sell a stock right away at the best price they can get
• You’ll make the trade, but you cannot be sure of the exact price
23. Limit Order
• You ask your broker to buy or sell a stock at a certain price or better
• You have control over the price, but the trade might not happen
24. Stop Loss Order

• You instruct your broker to sell a stock when its price drops to a level you set
• This helps you avoid losing too much money
25. Day Trading
• Traders buy and sell stocks on the same day
• They try to make money from small price changes that happen
26. Fundamental Analysis

• Looking at a company’s money situation and business outlook to figure out its stock worth
• Involves checking financial reports, industry shifts, and economic elements
27. Technical Analysis
• Studying number trends from trading to predict future price changes
• Uses graphs and other methods to spot patterns
28. Sector
• A bunch of stocks in the same field or business area
• Think tech, healthcare, and finance sectors
29. Earnings Per Share (EPS)

• A company’s profit split by the number of shares out there
• Helps to measure how much money a company makes
30. Beta

• This shows how much a stock’s price changes compared to the whole market
• When beta equals 1, the stock moves with the market, while higher or lower numbers mean it changes more or less than the market
31. Dividend Yield
• This is how much a company pays in yearly dividends as a percentage of its stock price
• Investors use this to compare how attractive different dividend-paying stocks are
32. Moving Average
• Traders use this tool to smooth out price data over a set time
• It helps spot trends and possible levels where prices might stop rising or falling
33. Resistance Level
• This is a price where a stock often stops going up
• Technical traders often see this as a good time to sell
34. Support Level
• A stock price where the stock stops falling
• Often gives technical traders a chance to buy
35. Market Maker
• A company ready to buy and sell a stock at public prices
• Helps the market stay liquid
36. Option
• An agreement that lets the buyer choose to buy or sell a stock at a set price within a specific time
• People use it to protect investments or make bets
37. Arbitrage
• Buying and selling securities at the same time in different markets to make money from price gaps
• Helps markets stay fair and balanced
38. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
• The total value of goods and services a country makes in a year
• A key sign of economic health that can affect stock markets
39. Inflation
• A widespread rise in prices and drop in money’s buying power
• Can influence stock values and how people invest
40. Exchange Rate
• How much one currency is worth when changed to another
• Matters to investors who work across borders and companies that do business worldwide
FAQs Section on Essential Stock Market Terms
Why is it important to understand stock market terms?
Understanding stock market terminology helps investors make informed decisions, communicate effectively with brokers and other investors, and analyze market trends more accurately.
How can I start learning these stock market terms?
Begin with the most important terms at the top of our list and gradually work your way down. Practice using these terms while reading financial news or discussing investments with others.
Are these all the terms I need to know to invest in the stock market?
While this list covers many essential terms, the stock market is complex, and there are always more concepts to learn. These 40+ terms provide a solid foundation for most investors.









