Technical analysis is a method used to predict future price movements in financial markets. It focuses on studying price and volume data from the past. Unlike fundamental analysis, which looks at a company’s business health, technical or fundamental analysis focuses on charts and patterns.

Technical Analysis is a trading methodology that uses historical price and volume data to predict market movements. Unlike fundamental analysis, technical analysis looks at statistical trends, chart patterns and market indicators to find trading opportunities. The approach is based on three core principles: price discounts everything (all known information is reflected in the price), prices trend and history repeats itself. The assumption underlying technical analysis is the presence of price trends. Technical analysts use various tools including price charts (candlesticks), volume indicators and technical indicators (moving averages, RSI, MACD) to make trading decisions. Not foolproof but technical analysis helps traders find entry and exit points, trends and manage risk through a systematic approach to market analysis.
Basic Principles
The Market Discounts Everything
Technical analysts believe that all known information is already reflected in market prices. This includes:
- Company news
- Economic factors
- Market sentiment
- Trader psychology
Price Movements Follow Trends
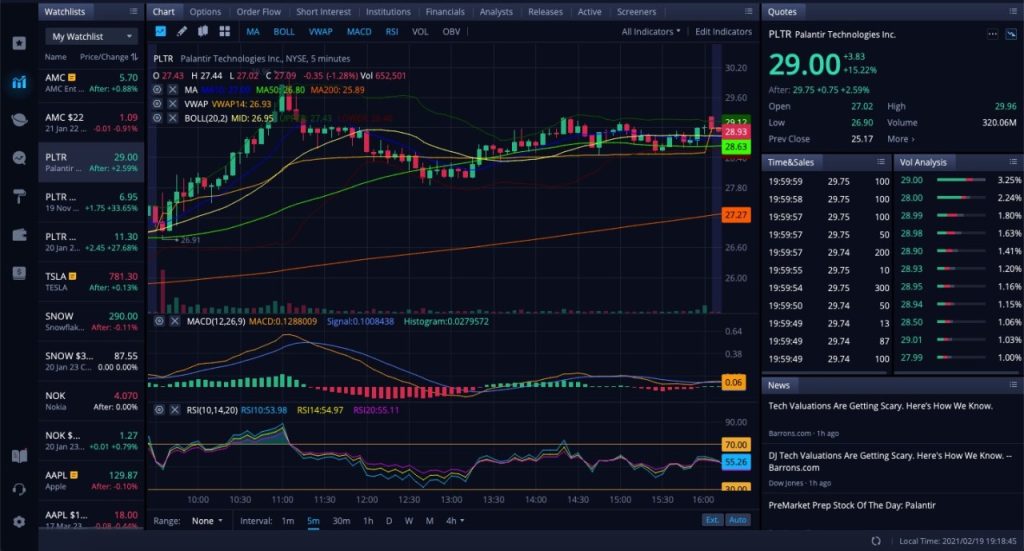
Markets tend to move in clear directions, or trends, which is the assumption underlying technical analysis. These can be:
- Upward (bullish)
- Downward (bearish)
- Sideways (consolidation)
History Tends to Repeat
Market behavior often shows similar patterns over time. This is linked to behavioral finance, which studies how emotions affect trading decisions.

Essential Tools and Charts
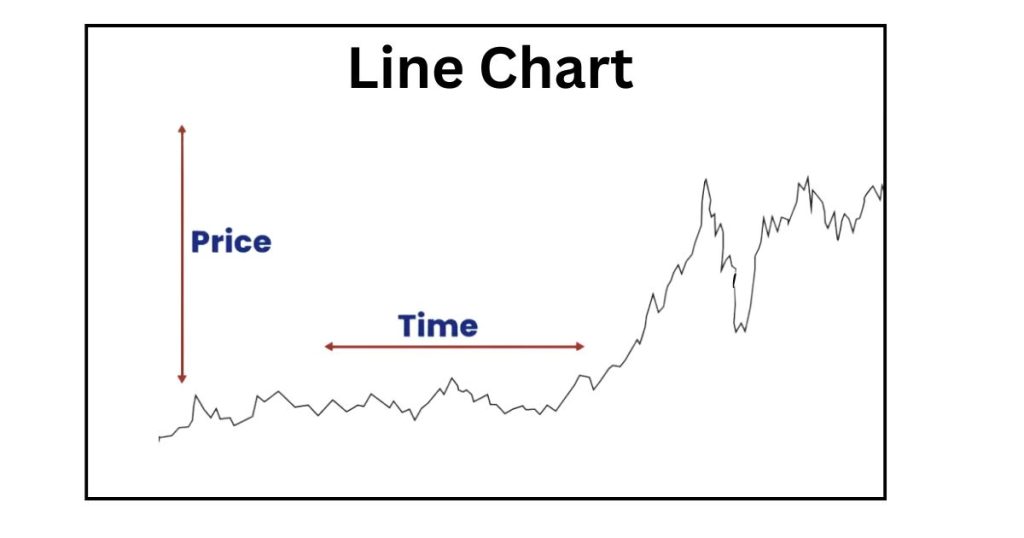
Types of Charts
- Line Charts
- Simplest form
- Shows closing prices connected by lines
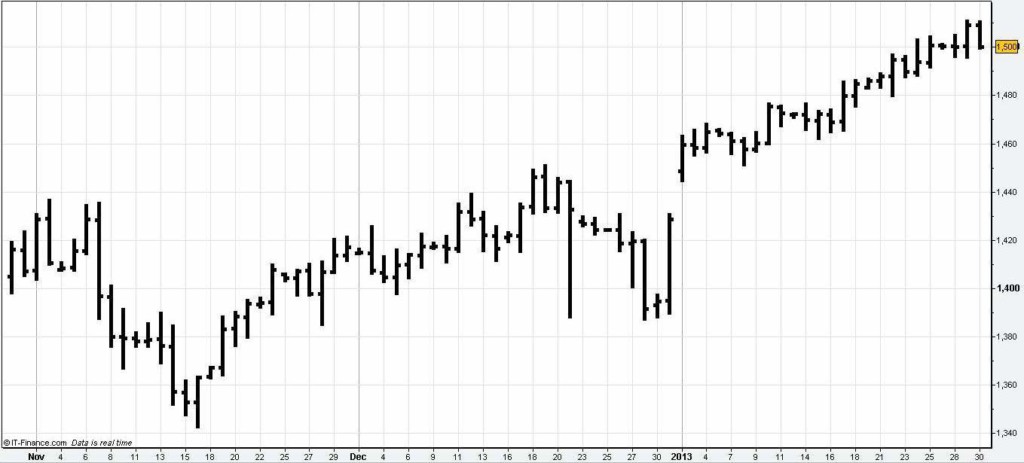
- Bar Charts
- Shows open, high, low, and closing prices
- Each bar represents one time period
- Candlestick Charts
- Most popular among technical traders
- Shows price action clearly
- Helps spot candlestick patterns
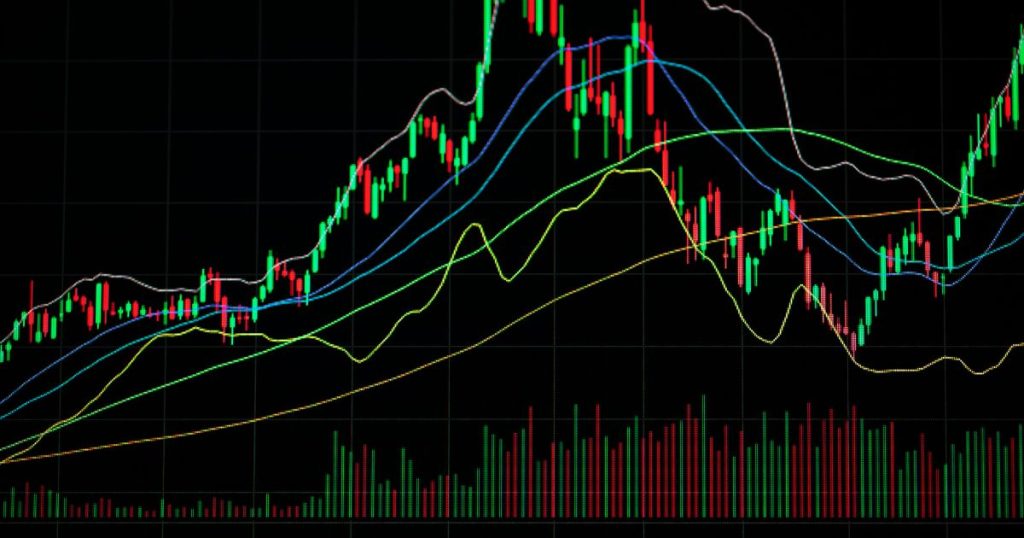

Key Technical Indicators
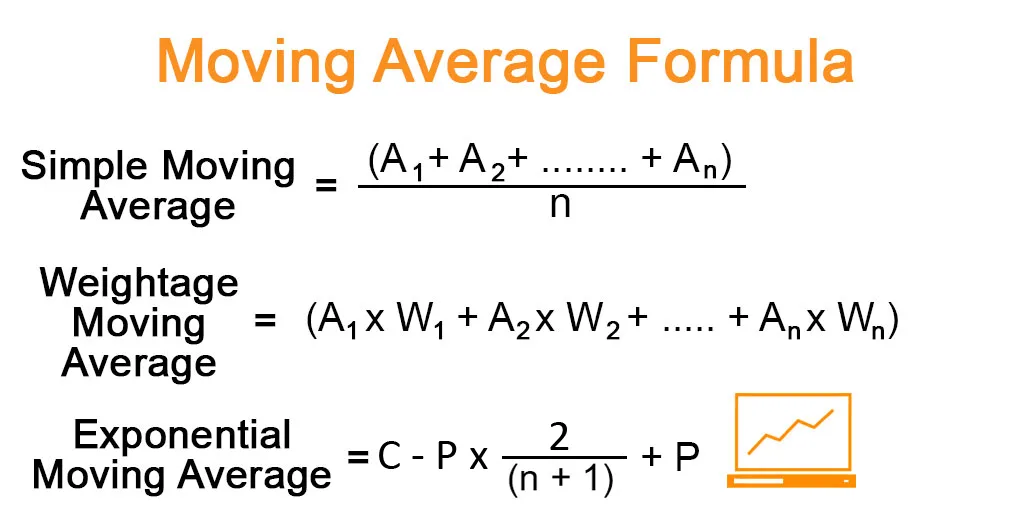
Moving Averages
- Help smooth out price data
- Show the average price over time
- Popular technical analysis tool for finding trends
- Types include:
- Simple moving average
- Exponential moving average
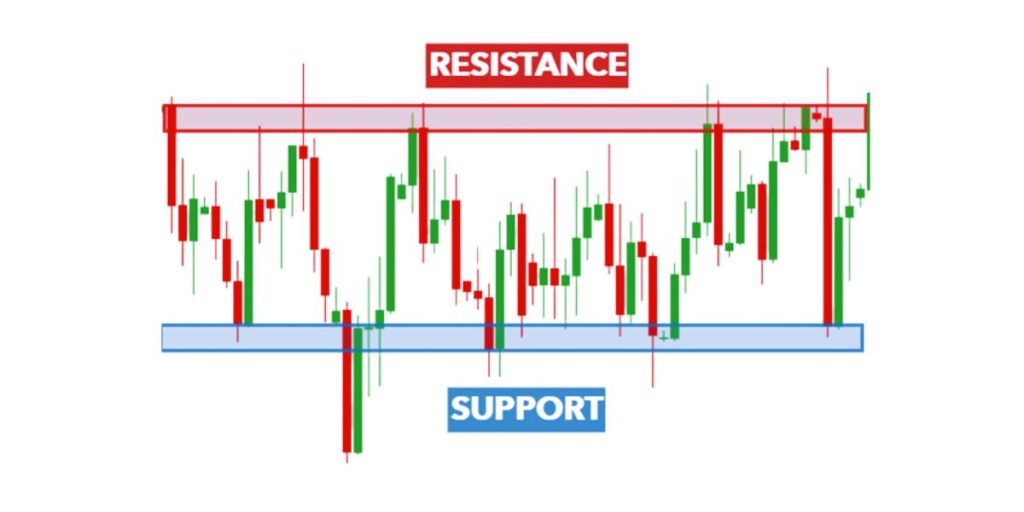
Support and Resistance Levels
- Support: Price level where buying usually occurs
- Resistance: Price level where selling usually occurs
- These levels help identify:
- Potential price reversals
- Trading opportunities
- Price targets
Advanced Concepts
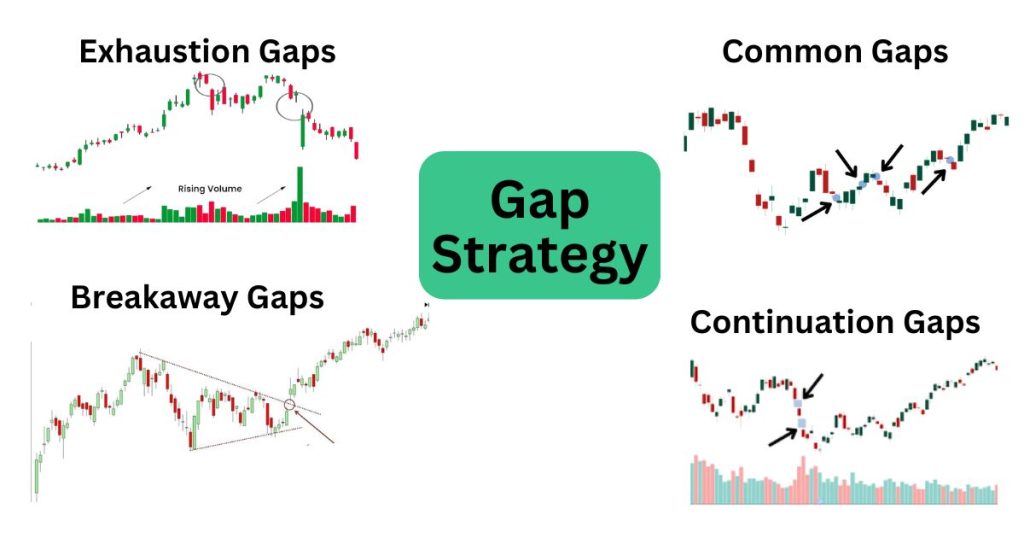
Price Gaps
These are empty spaces between trading periods on a chart. Gaps can signal:
- Strong market moves
- Changes in sentiment
- Potential trading opportunities
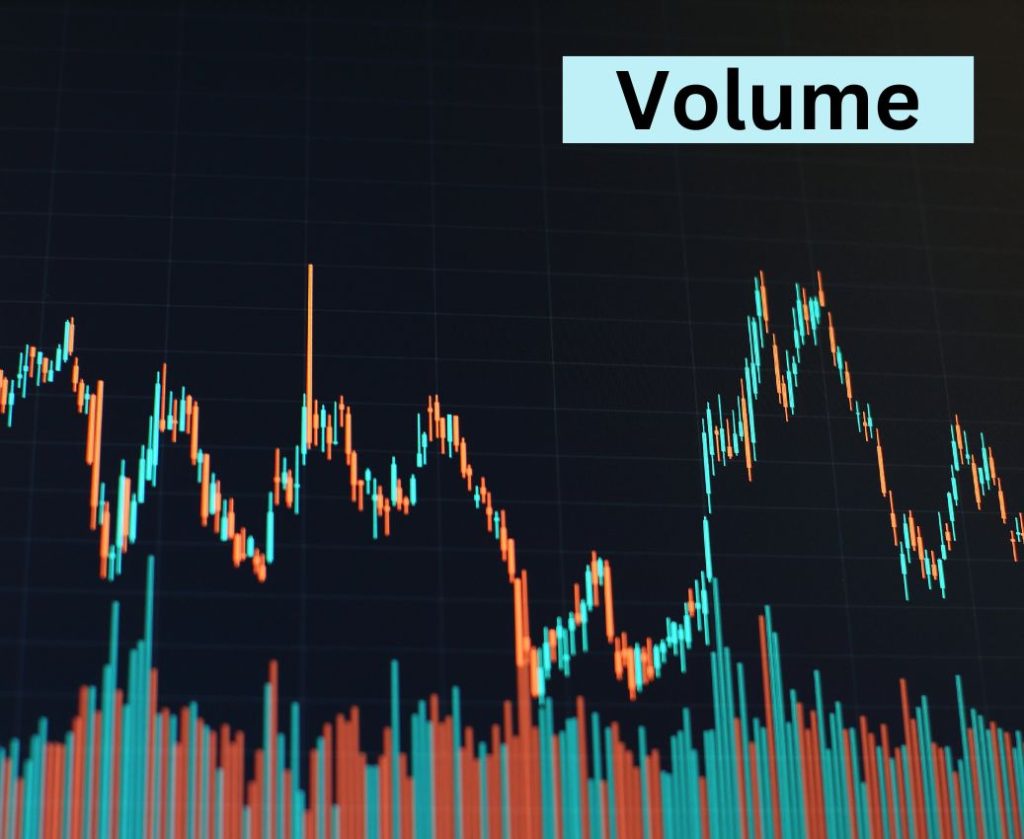
Volume Analysis
Volume is a key component of technical analysis. It helps:
- Confirm price trends
- Spot market strength
- Identify potential reversals
Statistical Trends
Technical analysts use various statistical tools to:
- Measure market momentum
- Calculate price-based indicators
- Generate trading signals
Trading Strategies
Developing a Trading Strategy
Successful technical traders:
- Combine multiple indicators
- Look for pattern confirmation
- Use proper risk management
- Study historical trading data
Market Sentiment Indicators
These tools help measure:
- Trader emotions
- Market psychology
- Potential market extremes
Professional Development
Becoming a Technical Analyst
- Study charting tools
- Learn technical indicators
- Understand market behavior
- Consider becoming a Chartered Market Technician (CMT)
Technical vs Fundamental Analysis
While fundamental analysts focus on intrinsic value and fair market value, traders using technical analysis or fundamental analysis concentrate on:
- Price patterns
- Chart analysis
- Market sentiment
- Trading methods
Asset Classes
Technical analysis works across various markets:
- Stocks
- Currencies
- Commodities
- Cryptocurrencies
Limitations and Considerations
Remember that technical analysis:
- Is not 100% accurate
- Should be part of a larger investment strategy
- Works best with other forms of analysis
- Requires constant learning and adaptation
Conclusion
Technical analysis is a powerful approach to understanding market movements. By studying price charts, patterns, and indicators, traders can make more informed decisions. Success requires practice, patience, and a solid understanding of both basic and advanced concepts.
Technical Analysis FAQs
Basic Understanding
What is technical analysis in simple terms?
Technical analysis is a trading method that predicts future price movement by looking at past market data, mainly price and volume. It’s like reading the market’s footprints to know where it will go next.
How is technical analysis different from fundamental analysis?
Fundamental analysis looks at a company’s intrinsic value through financials and economic factors, technical analysis looks only at price patterns, charts, and statistical indicators. Fundamental analysis answers “what to trade” while technical analysis answers “when to trade”.
What are the three main principles of technical analysis?
- Price discounts everything (all known information is in price)
- Price moves in trends
- History repeats itself
Technical Analysis Tools
What are the most common technical analysis tools?
Most used tools:
- Support and resistance
- Price charts (candlestick, line, bar)
- Technical indicators (Moving averages, RSI, MACD)
- Volume indicators
- Trend lines
What is the best timeframe for technical analysis?
There is no “best” timeframe – it depends on your trading style:
- Long term investors: Weekly to monthly
- Day traders: 1 minute to 1 hour
- Swing traders: 4 hour to daily
- Position traders: Daily to weekly
Are technical indicators reliable?
Technical indicators are tools, not crystal balls. Their reliability depends on:
- Trading strategy integration
- Market conditions
- Timeframe used
- Proper interpretation
- Confirmation from multiple indicators
Practical Application
How do I start learning technical analysis?
- Learn basic chart patterns and candlestick reading
- Learn price action basics
- Study major technical indicators
- Practice with paper trading
- Join trading communities or take structured courses
- Read books from technical analysts
Can technical analysis predict market crashes?
Technical analysis can’t predict crashes but can identify:
- Weakening market conditions
- Bearish patterns
- Divergences in indicators
- Unusual volume patterns. These can be signs of increased market risk.
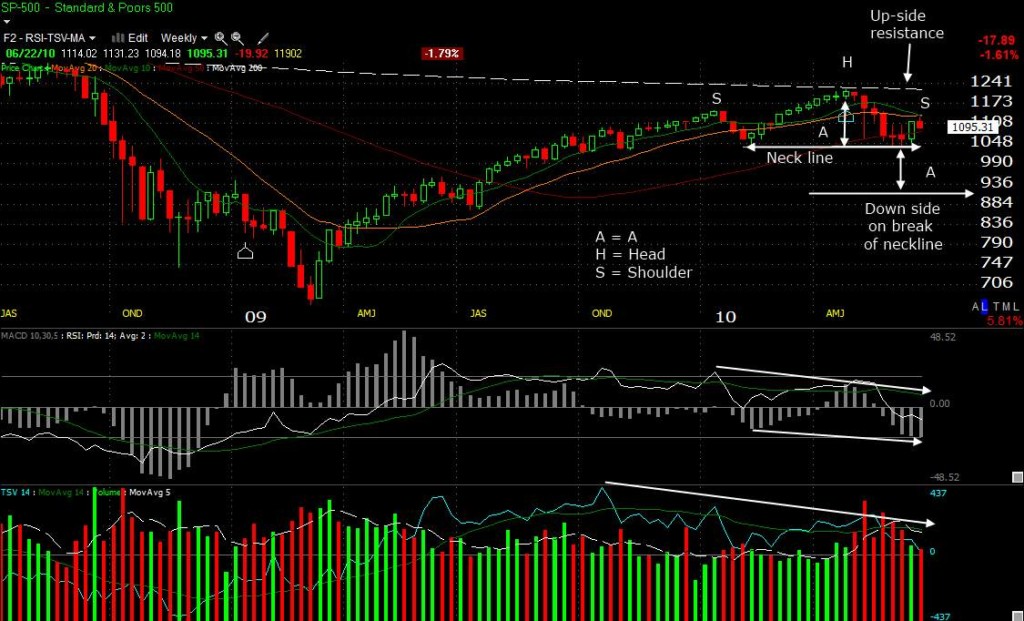
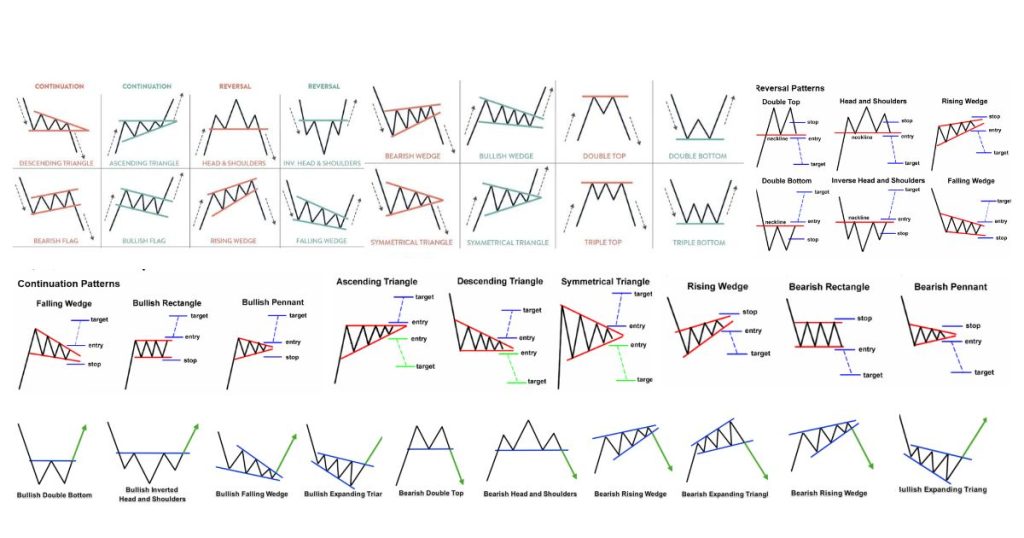
What are the most reliable chart patterns?
Most common reliable patterns:
- Head and Shoulders
- Double Tops and Bottoms
- Bull and Bear Flags
- Ascending and Descending Triangles. No pattern is 100% reliable – always use stop losses.
Advanced Concepts
How does psychology affect technical analysis?
Market psychology is important because:
- Patterns repeat because of similar trader reactions
- Support/resistance levels are often psychological price levels
- Volume shows the emotional intensity of traders
- Chart patterns are crowd behavior
Can technical analysis be automated?
Yes through:
- Algorithmic trading systems
- Trading bots
- Automated scanners
- Programming indicators. But human judgment is still needed for interpretation.
What are the limitations of technical analysis?
Main limitations:
- No guarantees
- Some indicators lag
- Subjective
- Market conditions affect effectiveness
- False signals
Best Practices
What is a successful technical analyst?
A successful technical analyst is:
- Disciplined
- Uses multiple timeframe analysis
- Combines different indicators
- Manages risk properly
- Keeps a trading journal
- Continuously learns and adapts
Should I use technical analysis alone?
It’s recommended to:
- Combine with fundamental analysis
- Consider market sentiment
- Watch economic events
- Monitor sector trends
- Stay informed about news
How many indicators should I use?
Best practice is:
- 2-3 core indicators
- No redundant indicators
- Include different types (trend, momentum, volume)
- Don’t overcrowd charts
- Keep it simple and clear
Risk Management
How does technical analysis help in risk management?
Technical analysis helps in risk management through:
- Stop-loss placement
- Position sizing
- Trend identification
- Market volatility assessment
- Entry/exit timing
What are technical analysis mistakes?
Common mistakes:
- Over-analyzing (paralysis by analysis)
- Using too many indicators
- Ignoring the bigger trend
- Not using stop losses
- Trading against the trend
- Forcing trades when conditions aren’t ideal
How reliable is technical analysis?
Technical analysis is reliable on:
- Strategy It’s not deterministic.
- Market conditions
- Timeframe
- Analyst’s experience
- Risk management